15 Jan The Role of Colonoscopy in Diagnosing Digestive Disorders
A colonoscopy is a procedure for examining the large intestine. This examination provides direct visual inspection of the colon and rectum, which allows for the accurate diagnosis of many conditions. Because it enables both diagnosis and treatment, this procedure helps manage digestive health. It offers a clear view of the intestinal lining, helping to identify issues that other tests might miss.
What is a Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a medical exam that uses a long, flexible tube called a colonoscope. The tube has a light and a tiny video camera on its end, and it sends images to a monitor. A doctor inserts the colonoscope into the rectum and carefully guides it through the entire colon to perform a thorough inspection. This method allows for a detailed visual assessment of the intestinal wall, while air or carbon dioxide is gently pumped into the colon to inflate it for a better view.
During the procedure, a doctor can perform several actions. Specialized tools are passed through a channel in the colonoscope, and these instruments remove abnormal growths or take small tissue samples. This capability makes the procedure both diagnostic and therapeutic. Patients are typically sedated to ensure comfort, and the exam itself usually lasts between 30 and 60 minutes. Proper preparation happens beforehand to clean out the colon, which ensures the doctor has a clear view.
What Are Digestive Disorders?
The procedure helps identify the causes of various intestinal issues. It helps doctors explore potential reasons for abdominal pain, chronic diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. A colonoscopy provides a direct view of insides. Such as the intestinal lining, which allows for the identification of swollen tissues, ulcers, and other irregularities that cause discomfort. This visual helps make a definitive diagnosis when symptoms are unclear.
Many chronic digestive conditions are diagnosed using this exam. For instance, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The doctor can see the location and extent of inflammation, and they can take tissue samples for analysis, which helps confirm the diagnosis. It remains a helpful tool for investigating a wide spectrum of intestinal problems.
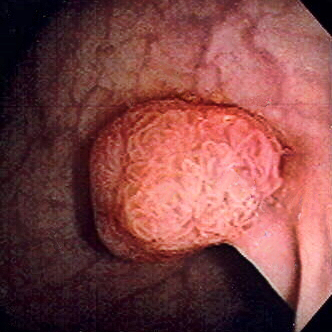
What is Colon Cancer?
One of the most important uses of a colonoscopy is for colon cancer screening. The procedure is highly effective at detecting precancerous polyps, which are abnormal growths on the colon’s lining. Since these polyps can develop into cancer over time, finding and removing them is a preventive measure. Early detection through regular screenings significantly reduces an individual’s risk of developing colon cancer.
Screening guidelines often recommend a colonoscopy for individuals starting at age 45, but those with increased risk factors may need to begin earlier. Risk factors include a personal or family history of colon cancer or polyps. If polyps are found and removed during a screening, a follow-up exam may be recommended to check for new growths. This proactive approach not only helps prevent cancer but also provides peace of mind, making it a part of long-term digestive wellness.
Make An Appointment
A colonoscopy is a fundamental procedure in the field of gastroenterology, and it offers significant diagnostic and preventive benefits. It provides an unmatched view of the large intestine, which allows for the accurate identification of various digestive disorders and the early detection of colon cancer. By enabling doctors to find and address issues before they become more serious, the exam saves lives and improves health outcomes. Regular screenings and timely diagnostic exams are key to maintaining digestive health and preventing severe disease.


No Comments